The US and Japan are approaching the level of last intervention! Rumors that the Bank of Japan is planning a major move in July?
With global economic fluctuations and continuous adjustments in monetary policy, the Bank of Japan's monetary policy meeting in July may bring a double surprise to the market - interest rate hikes and quantitative tightening. At present, the USD/JPY exchange rate is approaching the level of the Japanese government's last intervention.

The Blade of Inflation: The Double edged Sword Effect of Japanese yen depreciation
The performance of the Japanes
e yen in the international monetary market has always been a focus of attention for the Bank of Japan. Recently, the continuous depreciation of the Japanese yen has not only affected Japan's import costs, but may also push up inflation rates, far exceeding the central bank's target of 2%. This pressure has prompted the Bank of Japan to consider stabilizing monetary value through interest rate hikes and gradually withdrawing from its massive monetary stimulus policy through quantitative tightening.
The Bank of Japan issued a hawkish signal in its June meeting summary, hinting at the possibility of interest rate hikes. The members of the central bank's board of directors discussed the necessity of timely interest rate hikes to prevent excessive cost pressures from driving up inflation. This discussion is interpreted by the market as the central bank preparing for recent actions. President Kazuo Uchida stated after the meeting that there is a possibility of interest rate hikes next month, which further enhances market expectations.
The market generally expects that the Bank of Japan will announce a rate hike and reduce bond purchases at its July meeting, which will be a clear signal of the Bank of Japan's normalization of monetary policy. Raising interest rates may have a huge impact on the market, especially when it is launched simultaneously with a quantitative tightening plan. The Bank of Japan also plans to announce a specific plan on how to reduce large-scale bond purchases and shrink its balance sheet by $5 trillion.
When formulating a quantitative tightening plan, the Bank of Japan needs to strike a balance between exchange rate stability and bond market stability. The central bank may seek to increase its bond purchase cuts every quarter while retaining some flexibility to adjust the pace of cuts during market turbulence. This trade-off means that the Bank of Japan may announce a plan to reduce monthly bond purchases at a stable and fixed rate.
Three sources familiar with the Bank of Japan's ideas revealed that discussions within the Bank of Japan regarding interest rate hikes are very active, and they are considered as important topics in every policy meeting. They pointed out that although the market may have an impact on interest rate hikes and even trigger an economic recession, the Bank of Japan believes that under inflationary pressure, the current interest rate level is clearly too low. One of the sources emphasized that "interest rates are clearly too low" and suggested that "it is possible to raise interest rates in July", which largely depends on the upcoming economic data. Another source also believes that if the data shows sustained upward inflation, the Bank of Japan may take action in July. The third source echoed this view, believing that the central bank is preparing for possible interest rate hikes. The common view among these sources is that the Bank of Japan will closely monitor economic data when formulating monetary policy and be prepared to address inflation issues by raising interest rates if necessary.
The Bank of Japan may take a dual approach in July
Chief Economic Analyst at Tohoku Research, Kato Takashi, stated that the central bank must strike a balance between exchange rate stability and bond market stability. Therefore, the Bank of Japan may seek to increase its bond purchase cuts every quarter. If the yen continues to weaken, the Bank of Japan can simultaneously reduce bond purchases and raise interest rates in July. Simply reducing bond purchases may not be enough to prevent the yen from further falling.
From a technical analysis perspective, the USD/JPY exchange rate is approaching the level of the Japanese government's last intervention. On Tuesday (June 25th), Japanese Finance Minister Junichi Suzuki stated that he will closely monitor exchange rate fluctuations and continue to respond appropriately to excessive fluctuations in the foreign exchange market, hoping for a stable exchange rate trend.
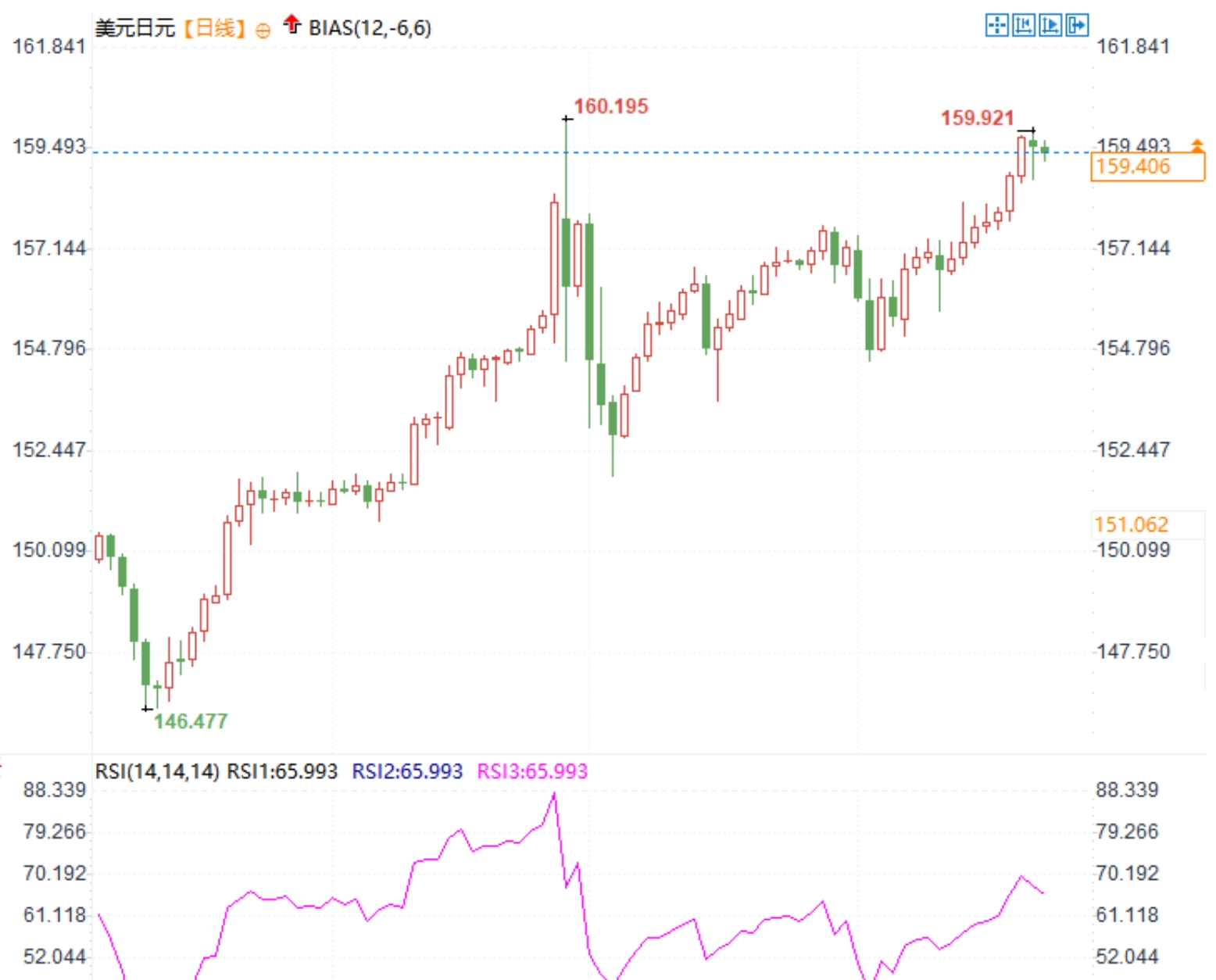
As the policy meeting on July 31st approaches, traders have intensified their bearish sentiment towards the Japanese yen. Once the Bank of Japan intervenes, the Japanese yen exchange rate may be affected and fluctuate. Raising interest rates usually attracts more foreign investors to purchase Japanese assets, as higher interest rates mean higher returns. This increases demand for the Japanese yen and may lead to its appreciation. Against the backdrop of other major central banks around the world continuing to implement loose monetary policies, the Bank of Japan's tightening policy may lead to policy differentiation, further enhancing the attractiveness of the yen.
The challenge facing the Bank of Japan is how to achieve normalization of monetary policy while maintaining exchange rate stability. The July meeting will be an important window to observe how the Bank of Japan balances these two major goals. Regardless of the outcome, this will be an important moment in the history of Japan's monetary policy.
Tips:This page came from Internet, which is not standing for FXCUE opinions of this website.
Statement:Contact us if the content violates the law or your rights
