Australia expects its budget deficit to widen before the 2025 election, with the first interest rate cut in April or May next year
The mid year fiscal update shows that due to increased government spending, the Australian budget is expected to fall further into deficit in the coming years, and the Australian general election will be held in less than six months.
According to the mid year economic and fiscal outlook released on Wednesday, although the budget gap for this fiscal year is expected to narrow slightly to AUD 26.9 billion (USD 17.1 billion), it will expand to AUD 46.9 billion by 2025-26, accounting for 1.6% of GDP and remaining at or above 1% of GDP. Due to rising interest rates dragging down private sector activity, the Ministry of Finance has also slightly lowered its economic growth expectations for this fiscal year and the next fiscal year.
The deterioration of accounting expectations is a blow to Finance Minister Jim Chalmers, who has been trying to establish a sound economic management narrative for the Labour government before the elections scheduled for May 17 next year.
He achieved consecutive surpluses in the first two budgets for the first time in nearly twenty years, but the increase in expenses damaged profits.
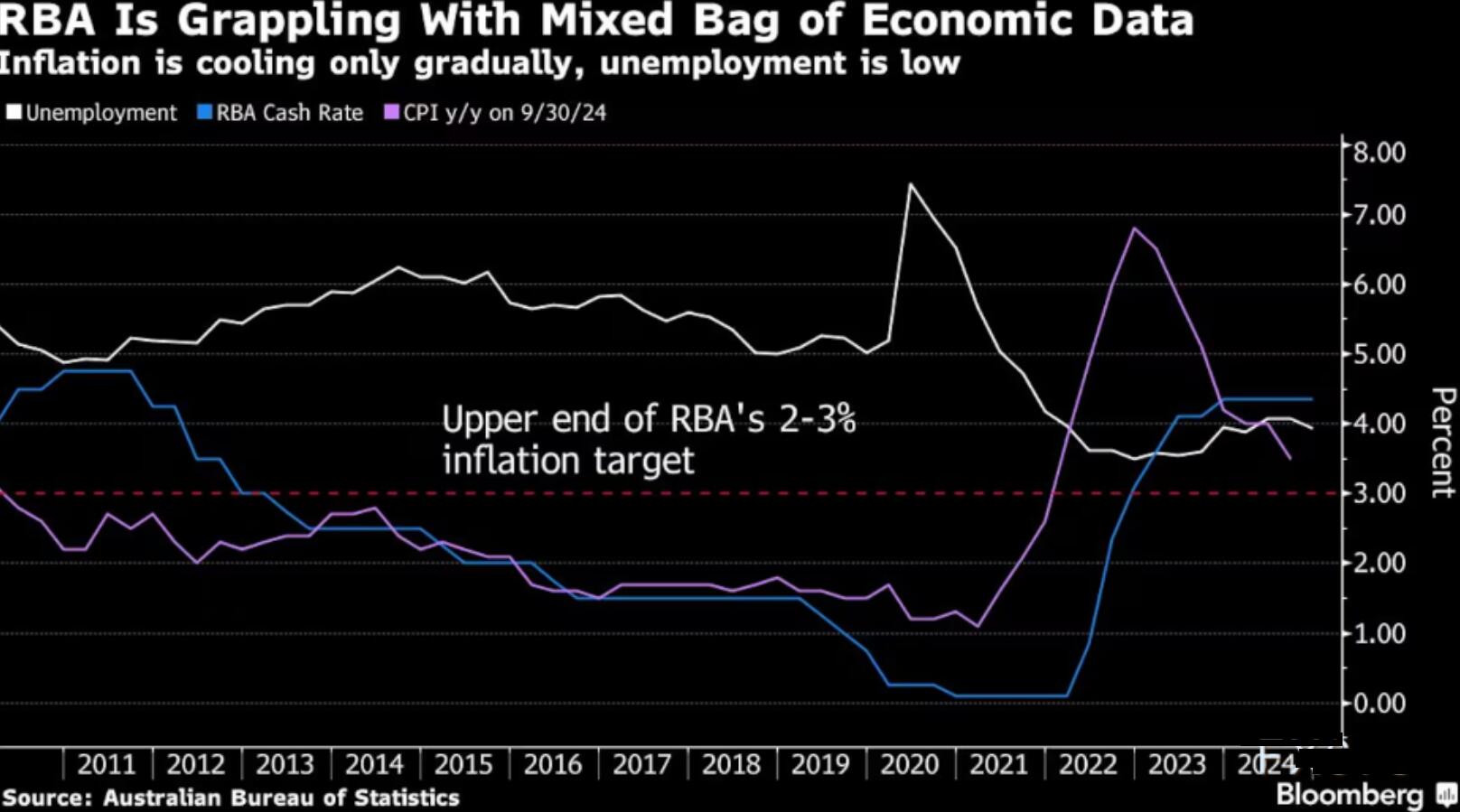
Public opinion polls show that voters are becoming increasingly frustrated with the country's economic situation, with interest rates reaching a 13 year high of 4.35% and prices still rising. Despite the government's attempts to alleviate the impact through cost of living reductions and tax cuts, dissatisfaction with the election still exists.
The budget update shows that payments are expected to grow faster than previously predicted, reflecting the government's efforts. Therefore, the proportion of net debt to GDP is expected to climb to 22.4% in 2027-28, compared to an estimated 21.9% in May.
The large influx of immigrants after the pandemic is expected to be a major factor in the 2025 election, and the latest budget shows that the government has failed to achieve its goal of significantly reducing net immigration.
The net number of overseas immigrants for this fiscal year has increased from 260000 in May to 340000. Subsequently, it is expected that the growth rate will slow down, partly due to the government's crackdown on international students.
The Ministry of Finance expects the inflation rate to remain within the target range of 2-3% set by the Reserve Bank of Australia, reflecting that energy rebates and other subsidies have lowered electricity and rental prices. Therefore, the central bank has shifted its focus to core inflation, which is currently at 3.5% and is expected to fall back to this range by the end of next year.
A broader deficit will give the Reserve Bank of Australia a headache as it tries to cool domestic demand and consumer prices. Economists have repeatedly stated that strong fiscal impulses are a key reason why central banks refuse to join the global easing cycle. The pricing in the money market means that the first interest rate cut will only occur in April or May next year.
Despite high interest rates, the unemployment rate remains at a very low level and is expected to climb to 4.5% by June 2025. Last week's data showed that the unemployment rate unexpectedly dropped to 3.9% in November, and the labor market is one of the strongest indicators for the government.
Tips:This page came from Internet, which is not standing for FXCUE opinions of this website.
Statement:Contact us if the content violates the law or your rights
