The Reserve Bank of Australia has more confidence in controlling inflation and is expected to cut interest rates for the first time in February
The minutes of the December meeting showed that the Reserve Bank of Australia is more confident in continuing to move inflation towards its target level, but given the recent rebound in consumption and the continued tightness of the labor market, it is too early to draw a conclusion that victory has been achieved.
The minutes of the meeting on December 9-10, released on Tuesday (December 24th), showed that the Reserve Board of Australia discussed plans to relax policies in the future to boost economic growth or maintain current restrictive levels. The council believes that both outcomes are possible and chooses to maintain the 4.35% interest rate unchanged, stating that recent data is not sufficient to change the policy outlook.
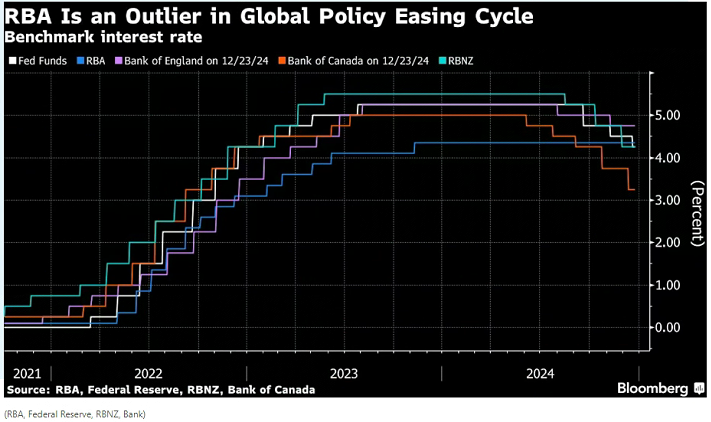
Image: Central Bank Benchmark Rate (The Reserve Bank of Australia is an outlier in the global policy easing cycle, with the blue line representing the Reserve Bank of Australia rate)
Council members pointed out that more information on employment, inflation, and consumption, as well as a revised set of staff forecasts, will be announced at the meeting on February 17-18, and hinted that the review may be real-time. Traders expect a probability of over two-thirds for the central bank to cut interest rates for the first time in February, and fully anticipate two rate cuts by July.
The meeting minutes show: "Members have assessed that since the last meeting, the risk of inflation returning to target levels slower than expected has decreased, and the downside risk of economic activity has increased. Members are wary of the risk that if labor demand in non market industries suddenly slows down, the increase in unemployment rate may exceed expectations
The minutes of the meeting drew attention to the thoughts of the board of directors for the month, during which the central bank governor, Brock, unexpectedly leaned towards the dovish camp. Due to the significant economic slowdown in most developed countries, Australia has been a global outlier in the current economic cycle. The Federal Reserve has sent a signal that it will cut interest rates twice more in 2025 on the basis of the three cuts already made this year.
At the same time, the meeting minutes also indicate that the Reserve Bank of Australia remains sensitive to the possibility of maintaining a strong consumer and job market, which is strong enough to thwart efforts to lower core inflation to target levels.
A private survey shows that consumer confidence in Australia has declined and remains pessimistic, even though the unemployment rate unexpectedly dropped to 3.9%, business confidence has deteriorated, highlighting Australia's mixed economic results in recent times.
The meeting minutes pointed out several factors and explained why policy makers believe that economic outcomes may have two scenarios:
1. Various employment indicators may indicate that progress towards full employment in the labor market has stalled
2. Preliminary signs of Black Friday sales indicate strong consumer demand
3. Global service price inflation has lasted longer than expected, and the situation in Australia may also be the same
4. In some cases, various risks to the global economic outlook may limit the pace of further deflation
There is also uncertainty regarding the level of policy restrictions, as the cash interest rate of the Reserve Bank of Australia remains lower than or equivalent to that of other developed economies.
The minutes of the meeting show that "despite interest rate cuts abroad, market expectations and central bank estimates of neutral interest rates suggest that monetary policies in several economies may be tighter than in Australia, and will remain so in 2025
The benchmark forecast of the Reserve Bank of Australia is that the unemployment rate will rise to 4.3% in December and reach a peak of 4.5% next year. The inflation indicator favored by the central bank, the adjusted mean, is expected to reach 3.4% by the end of this year and reach the upper limit of the 2-3% target range by mid-2025.
Tips:This page came from Internet, which is not standing for FXCUE opinions of this website.
Statement:Contact us if the content violates the law or your rights
